Medical Imaging Technology
|
 REMARK REMARK
This research was accepted as one of subjects in "Creation and Support Program for Start-ups from Universities" by Japan Science and Technology Agency. |
|
Adaptive Display Speed Control for Diagnosis of Capsule Endoscopic Images |
|
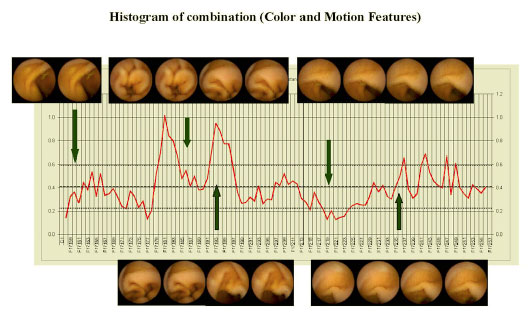 |
This work proposes a method for reducing diagnostic time by controlling frame rate adaptively in a capsule endoscopic image sequence captured during 8 hours. Depending on the skill, it requires from 45 minutes to two hours to evaluate the video sequence under extreme concentration of medical doctors. The video sequence would be played at high speed at stable regions to save time and the speed would be decreased at rough changing that can help suspicious findings more conveniently. The capturing conditions are classified into groups corresponding to changing levels between two frames. The delay time of these frames was calculated by the parametric function. The optimal parameter set is determined from evaluations by medical doctors. In conclusion, the average diagnostic time can be reduced from 8 hours down to around 30 minutes. |
|
|
|
Generating a Dissection Image of an Intestine |
|
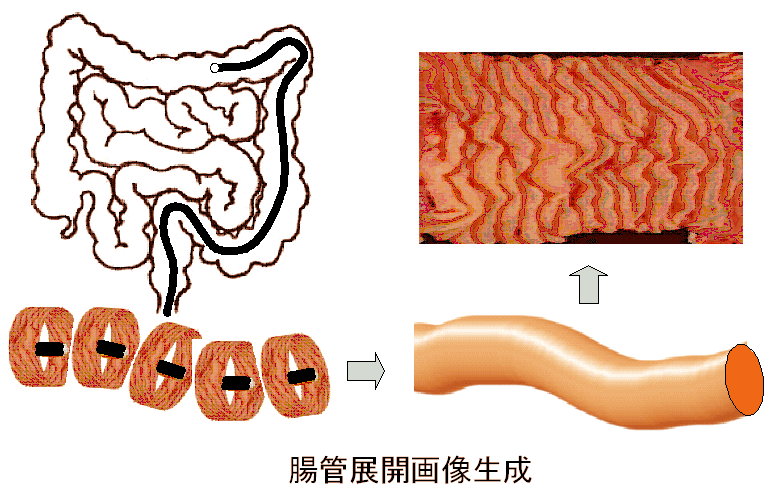 |
Diagnosis inside an intestine by an endoscope is difficult and time
consuming, because the whole image of the intestine cannot be taken at one time
due to the limited field of view. It is thus effective to generate a dissection image
which can be obtained by extending the image of an intestine. We acquire
an annular image sequence with an omnidirectional or wide-angle camera, and
then generate the dissection image by mosaicing the image sequence. Though
conventional mosaicing techniques transform an image by perspective or affine transformations,
these are not suitable for our situation because the target object is a
generalized cylinder and the camera motion is unknown a priori. Therefore, we
propose a novel approach for image registration that deforms images by a twodimensional-
polynomial function which parameters are estimated from optical
flow. We evaluated our method by registering annular image sequences and we
successfully generated dissection images.
|
|
|
| Calibration of Lens Distortion by using Gray-code Pattern Scanning |
|
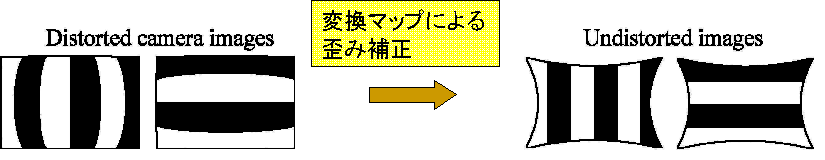 |
This research proposes a new method to automatically calibrate the lens distortion of wide-angle lenses. A map between the display coordinate system and the image coordinate one can be generated from capturing structured-light patterns on a flat display. This approach has two advantages. First, it is easier to take correspondences of image and marker (display) coordinates around the edge of a camera image than using a usual marker, e.g.a checker board. Second, since we can easily construct a dense map, a simple linear interpolation is enough to create an undistorted image. Our method is not restricted by the distortion parameters because it directly generates the map. |
|
|